 www.shednation.com
www.shednation.com Opening Ready to embark on a fulfilling DIY project? Building a 12x20 shed can provide valuable storage space, a workshop area, or even a small studio. This guide will walk you through the process, step-by-step, ensuring a sturdy and functional shed. Remember to check local building codes and obtain any necessary permits before starting.
Step 1: Planning and Preparation Before you start swinging a hammer, careful planning is crucial. Gather Materials: Create a detailed list of lumber, roofing materials, siding, hardware, and tools needed. Calculate the quantity accurately to avoid delays. Prepare the Site: Choose a level location for your shed. Clear any vegetation, debris, and obstacles. Consider drainage to prevent water damage. Design and Blueprints: While a 12x20 shed is a standard size, having a detailed plan or blueprints is essential. These can be found online or purchased from design services. These plans will include details for the foundation, framing, roofing, and siding.
Step 2: Building the Foundation A solid foundation is the bedrock of your shed. There are several options. A concrete slab is the most durable, but a gravel pad with concrete piers or a wooden skid foundation can also be effective. Concrete Slab (Option 1): Pour a 4-inch thick concrete slab, reinforced with rebar. Ensure it's level and properly cured. Gravel Pad and Piers (Option 2): Compact a gravel base. Dig holes for concrete piers, ensuring they are below the frost line. Pour concrete into the holes, embed post anchors, and level them. Skid Foundation (Option 3): Construct a frame from pressure-treated lumber. Level it on a bed of gravel, using shims as needed.
Step 3: Framing the Floor With the foundation in place, it's time to build the floor frame. Cut and Assemble the Frame: Using pressure-treated lumber, cut the joists and rim joists according to your plan. Assemble the frame using nails or screws. Ensure the frame is square and level. Install Floor Joists: Space the floor joists evenly, typically 16 inches on center. Secure them to the rim joists. Add Sheathing: Cover the floor frame with plywood or OSB sheathing. Secure the sheathing with nails or screws.
Step 4: Framing the Walls This step involves constructing the walls of the shed. Cut Wall Studs and Plates: Cut the wall studs, top plates, and bottom plates according to your plan. Assemble Wall Frames: Assemble the wall frames on the floor, nailing or screwing the studs to the top and bottom plates. Ensure the walls are square. Include openings for doors and windows. Raise and Secure Walls: Raise the wall frames one by one, bracing them temporarily. Secure them to the floor frame and to each other at the corners. Use a level to ensure the walls are plumb.
Step 5: Installing the Roof The roof protects your shed from the elements. Install Rafters or Trusses: Install rafters or trusses according to your plan. Ensure they are properly spaced and securely fastened to the walls. Add Roof Sheathing: Cover the rafters or trusses with plywood or OSB sheathing. Secure the sheathing with nails or screws. Apply Roofing Material: Install roofing felt or underlayment, followed by your chosen roofing material (shingles, metal, etc.). Follow the manufacturer's instructions for proper installation.
Step 6: Adding Siding and Trim Siding protects the walls and adds to the aesthetic appeal. Install Siding: Install your chosen siding material (wood, vinyl, metal) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Overlap the siding properly to prevent water penetration. Add Trim: Install trim around the doors, windows, and corners to cover gaps and provide a finished look.
Step 7: Installing Doors and Windows Doors and windows provide access and natural light. Install Door Frame: Install the door frame according to the manufacturer's instructions. Ensure it's plumb and square. Hang the Door: Hang the door, ensuring it swings smoothly and latches properly. Install Windows: Install the windows according to the manufacturer's instructions. Seal around the windows to prevent drafts and water leaks.
Step 8: Interior Finishing (Optional) You can customize the interior of your shed to suit your needs. Insulation: Insulate the walls and roof to regulate temperature and reduce condensation. Electrical Wiring: If desired, install electrical wiring for lighting and power outlets. This should be done by a qualified electrician. Interior Walls and Flooring: Add interior walls and flooring as needed to create separate spaces or a finished look.
Conclusion Building a 12x20 shed is a significant undertaking, but with careful planning, diligent work, and adherence to safety precautions, you can create a valuable and functional structure. Enjoy the satisfaction of building your own shed!
12x20 Sheds: Complete Guide
 shedsunlimited.net
shedsunlimited.net 12x20 Executive Barn With Loft
 hartvilleoutdoorproducts.com
hartvilleoutdoorproducts.com Best Barns Belmont 12x20 Wood Shed
 www.shednation.com
www.shednation.com 

![Cedarshed studio 12x6 shed [st126]](https://i0.wp.com/www.shednation.com/oscthumb.php?src=/images/cedarshed/cedarshed-studio-shed-st96-1.jpg&w=1500&h=1220&f=jpg&q=95&hash=a1b196bdc5513eb64d7a831305149a4c) www.shednation.com
www.shednation.com  ilikesheds.com
ilikesheds.com  www.walmart.com
www.walmart.com  www.mysheds.com
www.mysheds.com  www.wayfair.co.uk
www.wayfair.co.uk  www.vecteezy.com
www.vecteezy.com  mysticalnumbers.com
mysticalnumbers.com  ar.inspiredpencil.com
ar.inspiredpencil.com  www.redfin.com ```html
www.redfin.com ```html  unsplash.com
unsplash.com  www.homebazaar.com
www.homebazaar.com  infoupdate.org
infoupdate.org  www.housedesignideas.us
www.housedesignideas.us  www.housedesignideas.us
www.housedesignideas.us  designstripe.com
designstripe.com  detailingshed.com.au
detailingshed.com.au  detailingshed.com.au
detailingshed.com.au  www.cleanwaterstore.com
www.cleanwaterstore.com 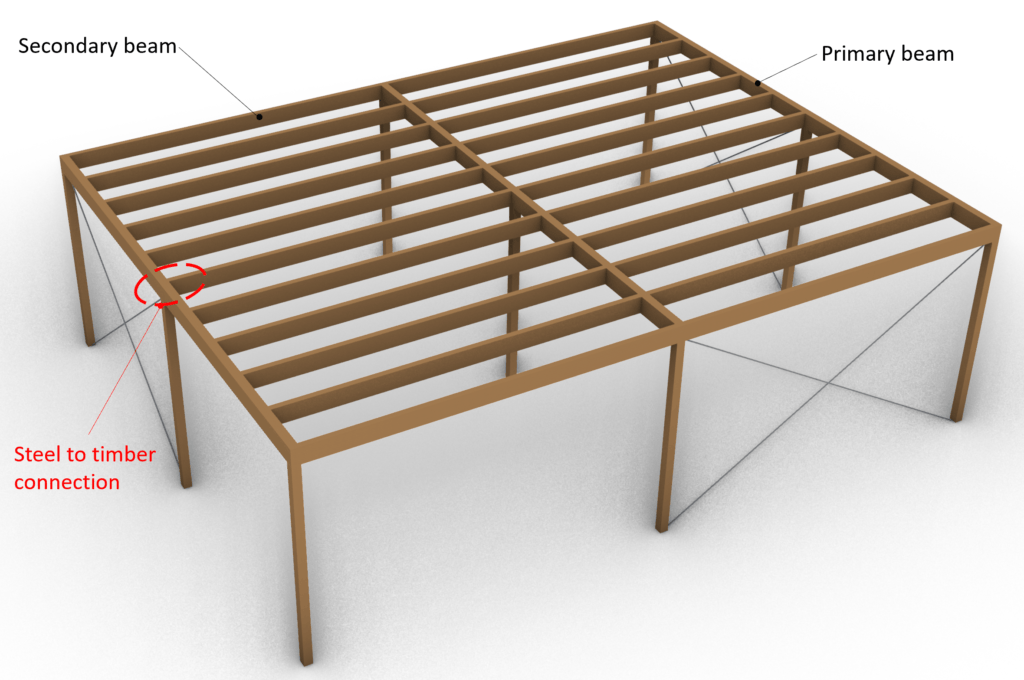 www.structuralbasics.com
www.structuralbasics.com  www.pinterest.com
www.pinterest.com  www.pinterest.com.au
www.pinterest.com.au  sheddrafts.com
sheddrafts.com  shedtrussdesignfree.blogspot.com
shedtrussdesignfree.blogspot.com  naruto-gratis.blogspot.com
naruto-gratis.blogspot.com  www.pinterest.com
www.pinterest.com  yardshedkitscostco.blogspot.com
yardshedkitscostco.blogspot.com  www.homecrux.com
www.homecrux.com